Description
A syringe is a medical tool used to inject liquid medications or other liquid substances into or extract fluids from body tissues.
Injecting drugs: A doctor or nurse uses a syringe to inject drugs directly into a patient’s muscles, blood vessels, or subcutaneous tissues to treat an illness or provide first aid.
Drawing blood: A medical professional uses a Phlebotomizer (a special type of syringe) to draw blood from a patient for testing or diagnosis.
Infusion: Syringes are also used to deliver fluids into a patient’s venous system to maintain fluid balance or to deliver medications.
Products details:
Size:1ml,2ml,3ml,5ml,10ml,20ml,30ml,50ml,60ml,100ml,120ml
Syringe top:Luer slip or luer lock
Syringe packing:Blister peel or pouch Tear polybag
Structural part:Three parts,Syringe barrel,Syringe plunger,Syringe Plugs
Needle Size:12Guage-34Guage
Components of a syringe:
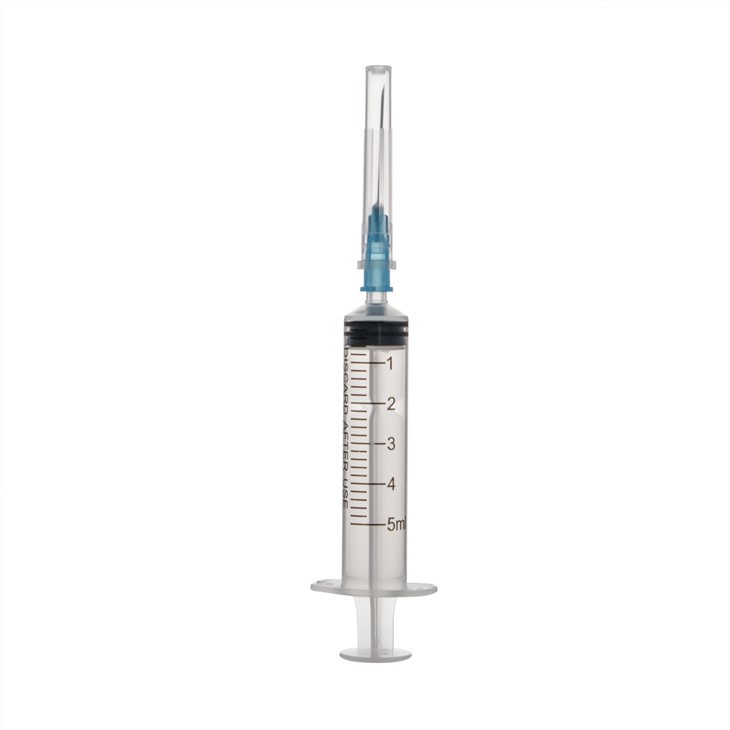
Barrel: A barrel is a hollow, tubular structure, usually made of clear plastic or glass, that holds a liquid medication. The barrel usually has graduated lines on it to measure the volume of the liquid.
Piston (Plunger): The piston is the moving part inside the cartridge and is usually made of rubber or plastic. By moving the piston, the volume of liquid can be changed within the cartridge.
Needle: A needle is a metal tube attached to the bottom of the cartridge that is used to inject or withdraw liquid from the body. Needles usually have a sharp tip to easily penetrate skin and tissue.
Needle Cap: This is a cap that protects the needle and is usually made of plastic. It is used to cover the needle before and after use to ensure hygienic performance of the syringe.
Plunger Rod: The Plunger Rod is the part attached to the piston that pushes or pulls the piston to control the flow of liquid.
Nozzle: The nozzle is the end of the syringe that is used to release the liquid. In disposable syringes, there is usually no nozzle, while in multi-use syringes, the nozzle may be replaceable.
Product Specifications:
| CODE | Descripition | Syringe top | Packing | Structural part | Needle Size |
| TYL101 | Syringe 1ml ,With needle | 1.luer slip top 2.luer lock top |
1.Blister peel 2.pouch Tear polybag | 1.Two parts:Syringe barrel,Syringe plunger 2.Three parts:Syringe barrel,Syringe plunger,Syringe Plugs |
16Guage-34Guage |
| TYL201 | Syringe 1ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL102 | Syringe 2ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL202 | Syringe 2ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL103 | Syringe 3ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL203 | Syringe 3ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL104 | Syringe 5ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL204 | Syringe 5ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL105 | Syringe 10ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL205 | Syringe 10ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL106 | Syringe 20ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL206 | Syringe 20ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL107 | Syringe 30ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL207 | Syringe 30ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL108 | Syringe 50ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL208 | Syringe 50ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL109 | Syringe 60ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL209 | Syringe 60ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL110 | Syringe 100ml ,With needle | ||||
| TYL210 | Syringe 100ml ,Without needle | ||||
| TYL111 | Insulin syringe 0.5ml/1ml |
Product detail:

Using:
Syringes can also be used in medical devices, containers, and scientific instruments such as some in chromatography to inject through rubber septa. Injecting gas into a blood vessel will cause an air embolism. The way to remove air from the syringe to avoid embolism is to turn the syringe upside down, tap it lightly, and squeeze out a little bit of fluid before injecting into the bloodstream.
In some cases where accuracy is not the primary concern of germs, such as quantitative chemical analysis, glass syringes are still used due to the small error of the glass syringe and the smooth movement of the push rod.
You can also inject some of the juices into meat with a syringe to improve taste and texture while cooking, or into pastries when baking. Syringes can also fill ink cartridges with ink.
Specifications:
Generally, 2 ml, 5 ml, 10 ml or 20 ml syringes are used, occasionally 50 ml or 100 ml syringes are used for intradermal injection.
Syringes can be made of plastic or glass and usually have a scale indicating the volume of liquid in the syringe. Glass syringes can be sterilized with autoclaves, but because plastic syringes are cheaper to dispose of, modern medical syringes are mostly made of plastic, which further reduces the risk of blood-borne diseases. Reuse of needles and syringes is associated with the spread of diseases, particularly HIV and hepatitis, among intravenous drug users.